Heretic: Fully Automatic Censorship Removal for Language Models via Optimized Abliteration
A Python tool that removes safety alignment from transformer-based language models without expensive post-training. Combines directional ablation with TPE-based parameter optimization via Optuna to produce decensored models that rival manual expert abliterations — in about 45 minutes on an RTX 3090.
Fully automatic censorship removal for language models
Abliteration — the technique of removing safety alignment from language models by identifying and suppressing "refusal directions" in transformer weight matrices — has been around since Arditi et al.'s 2024 paper. But until now, doing it well required understanding transformer internals and manually tuning parameters. Heretic, by Philipp Emanuel Weidmann, makes the process fully automatic.
The tool implements a parametrized variant of directional ablation combined with a TPE (Tree-structured Parzen Estimator) optimizer powered by Optuna. It co-minimizes two objectives: the number of refusals on "harmful" prompts and the KL divergence from the original model on "harmless" prompts. The result is a decensored model that refuses less while retaining as much of the original model's intelligence as possible.
// How It Works
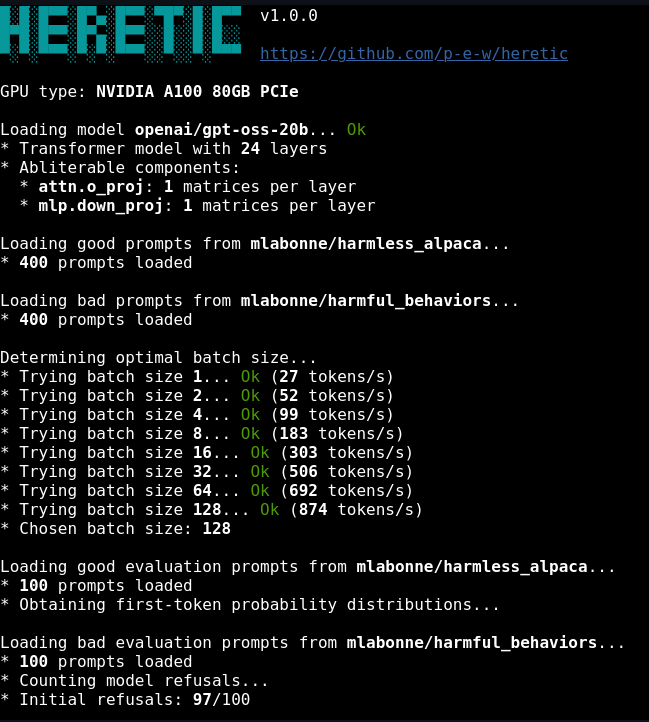
For each supported transformer component (attention out-projection and MLP down-projection), Heretic identifies the associated matrices in each layer and orthogonalizes them with respect to the computed "refusal direction." Refusal directions are calculated as a difference-of-means between first-token residuals for harmful and harmless example prompts.
The ablation process is controlled by several optimizable parameters that define the shape of an ablation weight kernel across layers: max_weight, max_weight_position, min_weight, and min_weight_distance. Rather than applying uniform ablation across all layers (as simpler implementations do), Heretic optimizes a flexible weight curve that applies different strengths at different layers.
// What Makes It Different
// Benchmark Results
The README includes a comparison on Gemma 3 12B Instruct that demonstrates the approach. All abliterated models achieve the same refusal suppression (3/100 refusals vs. 97/100 for the original), but differ significantly in how much they diverge from the original model's behavior on harmless prompts:
| Model | Refusals (of 100) | KL Divergence |
|---|---|---|
| gemma-3-12b-it (original) | 97 | 0 (baseline) |
| mlabonne/gemma-3-12b-it-abliterated-v2 | 3 | 1.04 |
| huihui-ai/gemma-3-12b-it-abliterated | 3 | 0.45 |
| p-e-w/gemma-3-12b-it-heretic | 3 | 0.16 |
The Heretic version achieves the same 3/100 refusal rate as manually-tuned abliterations, but at a KL divergence of 0.16 — roughly one-third of the next best result and one-sixth of the established mlabonne abliteration. Lower KL divergence means less damage to the model's general capabilities. These results were generated with default settings and no human intervention.
// Usage
The tool is designed to be as simple as possible. With Python 3.10+ and PyTorch 2.2+ installed:
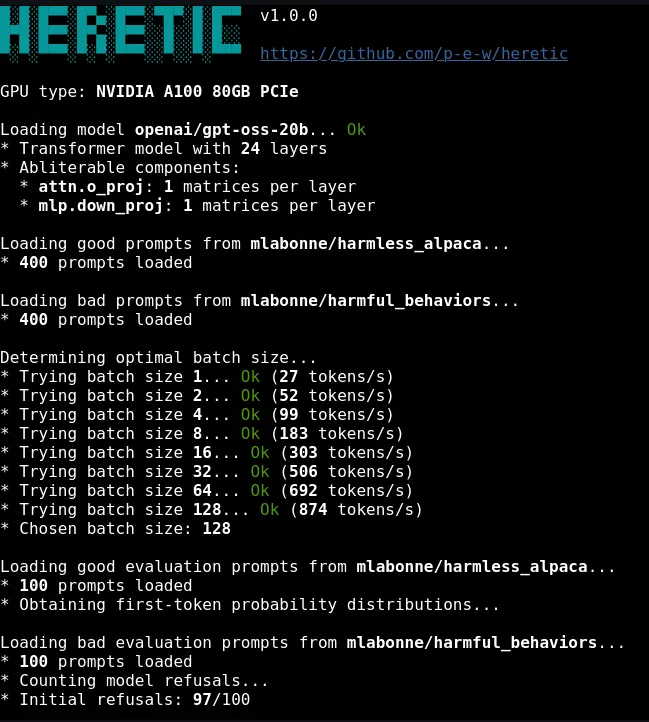
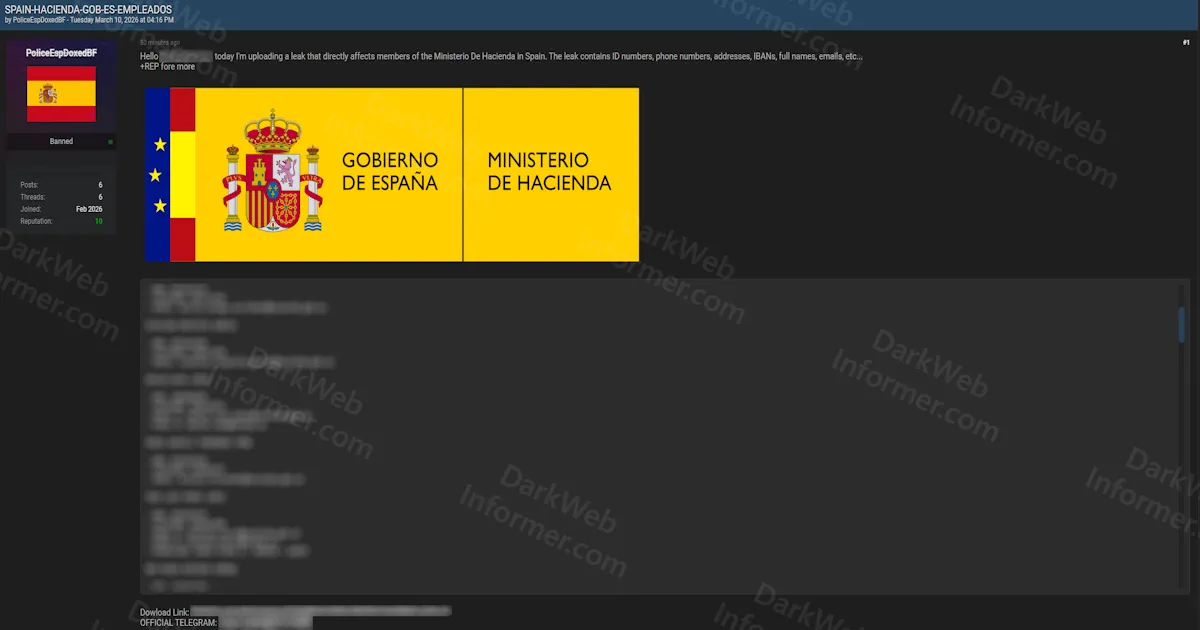
Heretic benchmarks the system at startup to determine optimal batch size. After processing, it offers to save the model locally, upload to Hugging Face, or open an interactive chat session for testing. A collection of pre-made models is available on Hugging Face under the "The Bestiary" collection.
// Model Compatibility
// Considerations
Hardware requirements. Decensoring requires loading the full model into GPU memory for the optimization process. Larger models (70B+) will require multi-GPU setups or quantization approaches. The ~45 minute benchmark is for an 8B model on an RTX 3090.
Quality variability. Results depend on the base model architecture, the prompt datasets used for computing refusal directions, and how the original model was safety-tuned. The Gemma 3 12B results are strong, but performance may vary across different model families.
AGPL-3.0 license. The tool is licensed under the GNU Affero General Public License v3.0, which requires that any modifications or derivative works be released under the same license. This is a strong copyleft license that has implications for commercial use.
Evaluation limitations. The refusal and KL divergence metrics provide useful signal but don't capture everything. A model that passes these metrics could still have subtle capability degradation, or conversely, could still refuse in ways not captured by the test prompts.
// Bottom Line
Heretic represents a significant step in abliteration tooling. The combination of fully automatic operation, TPE-based parameter optimization, flexible weight kernels, and interpolated refusal directions produces results that match or exceed manual expert work — with zero human effort. The two-line install-and-run workflow makes it accessible to anyone who can use a command line.
The 7.9k stars and 799 forks in a short period reflect strong demand for this kind of tooling. Whether you view that as a win for open research and user autonomy or a concern for AI safety depends on where you sit in the alignment debate. Either way, Heretic is a technically impressive tool that's worth understanding.